Working principle of carbon dioxide laser cutting machine
The working principle of a carbon dioxide laser cutting machine is based on the process of laser generation, focusing, and material interaction, which can be divided into the following steps:
1、 Laser generated
Proportion of working substance and gas:
The discharge tube of the laser is filled with a mixture of gases such as CO ₂, N ₂, He, etc., with a typical ratio of CO ₂: N ₂: He=1:0.5:2.5, and a total pressure of about 1066.58 Pa. These gases are excited by electrical energy, causing CO ₂ molecules to transition to high-energy states.
Energy level transition and laser release:
When CO ₂ molecules return from a high-energy state to a low-energy state, they release infrared photons with a wavelength of 10.6 micrometers. These photons are repeatedly reflected and amplified within the resonant cavity, ultimately forming a high-intensity and highly directional laser beam.
2、 Laser focusing and cutting
Optical system focusing:
The laser beam is guided through a reflective mirror (such as a gold-plated or selenized mirror) and then focused into a high-energy spot by a focusing mirror (commonly with a focal length of 2.5 inches or 4 inches). Energy is highly concentrated and can quickly heat materials in extremely small areas.
Material melting and gasification:
When a high-energy laser beam is irradiated onto the surface of a material, the local temperature rises sharply, causing the material to instantly melt or vaporize. For metal materials, laser power usually needs to reach 1000W-4000W to achieve effective cutting; Non metallic materials such as wood and acrylic can be used with lower power (30W-500W).
Gas assisted blowing of slag:
Compressed gas (such as oxygen, nitrogen, or compressed air) coaxial with the laser beam blows away melted or vaporized materials to form clean and precise cuts. Oxygen is commonly used to cut metals to enhance oxidation reactions, while nitrogen is used to prevent material oxidation (such as stainless steel cutting).
3、 Numerical Control System Control
Automated path planning:
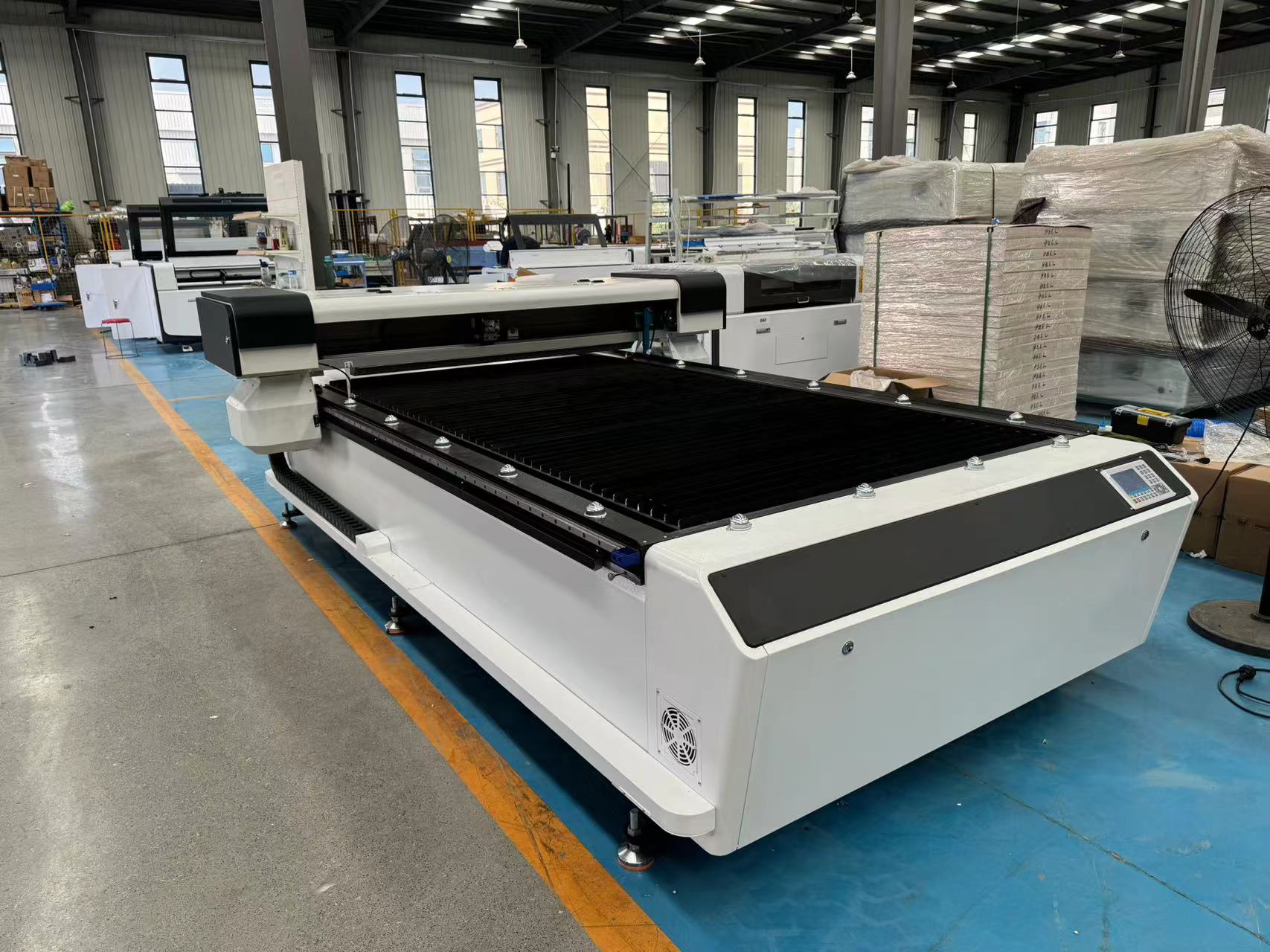
The numerical control system (PC or PLC) controls the laser head to move along the X-Y axis based on preset CAD drawings, achieving automated cutting of complex graphics. The cutting speed can reach over 100m/min, and the repeated positioning accuracy is ± 0.025mm.
Parameter dynamic adjustment:
Through supporting software such as RDWorks and LaserCut, laser power, cutting speed, gas pressure and other parameters can be adjusted in real time to meet the cutting needs of different materials (such as metal, non-metal) and thicknesses (such as<12mm low-carbon steel plate,<6mm stainless steel plate).
4、 Core components and auxiliary systems
Tipo de láser:
Glass tube laser: power range of 30W-500W, lifespan of about 2000-10000 hours, low cost, suitable for non-metallic cutting.
Metal RF tube laser: has a longer lifespan (up to tens of thousands of hours), higher stability, but is more expensive and commonly used for high-precision machining.
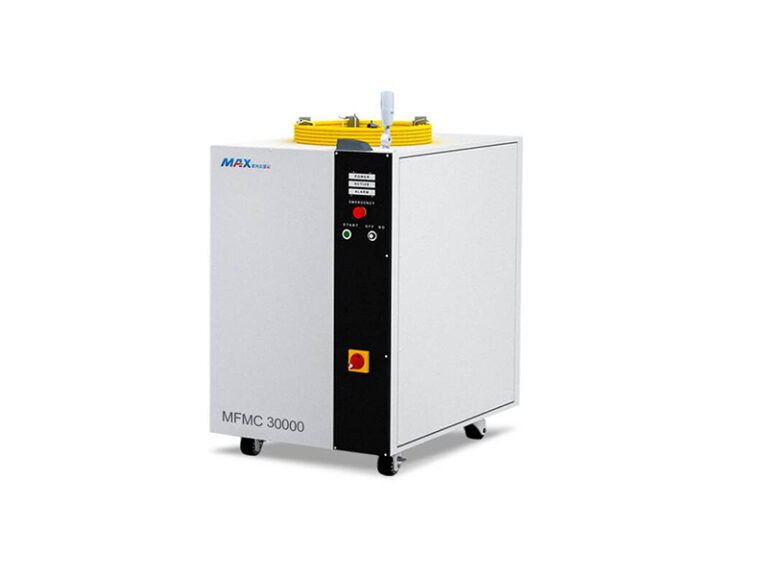
Cooling system:
High power lasers require a water cooling system (such as circulating cooling water) to prevent overheating of the laser; Low power models can use air cooling.
Security protection:
Wear protective goggles during operation to avoid direct laser exposure to the eyes.
When processing chlorine containing materials such as PVC, strong smoke exhaust is required to prevent the accumulation of toxic gases.
Equip fire extinguishers and monitor the entire process of processing flammable materials.