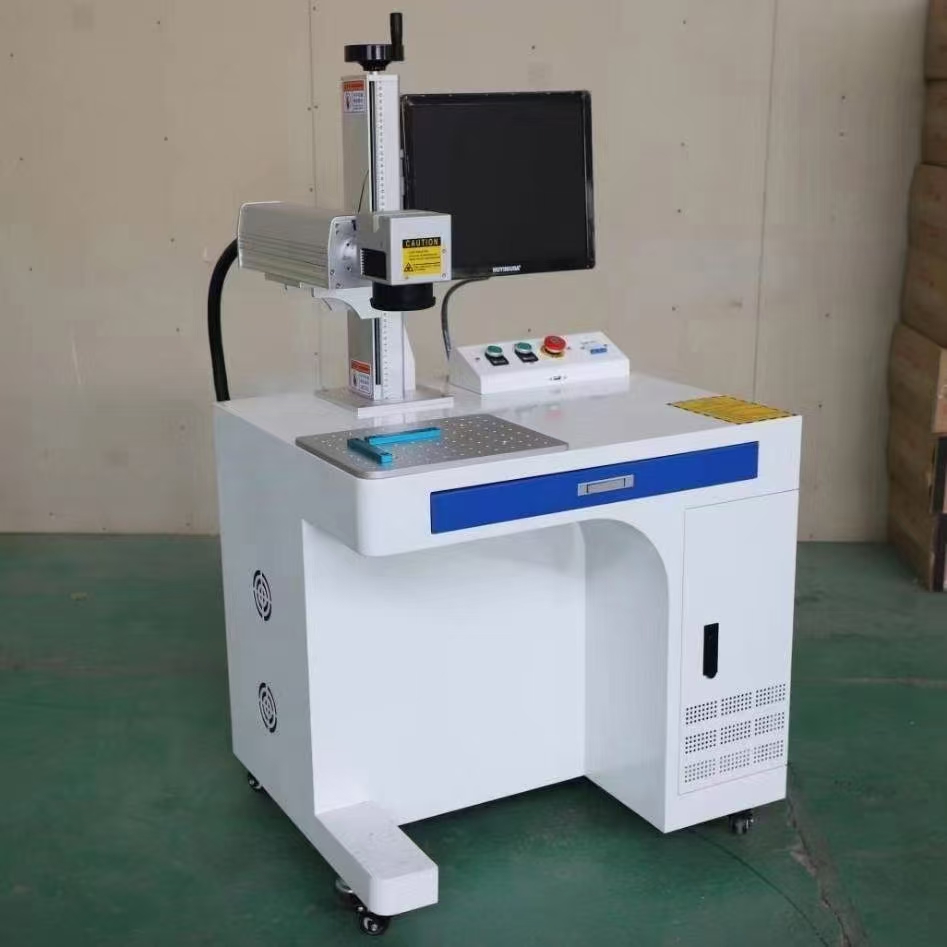
Core principle of fiber laser marking machine
The core principle of fiber laser marking machine is to use a high-energy density laser beam to locally irradiate the surface of the material, and through the interaction between light energy and the material, cause physical or chemical changes, thereby forming permanent marks. The following provides a detailed explanation from four aspects: fundamental principles, operational processes, key components, and marking effects:
1、 Basic Principles: Generation and Characteristics of Laser
The core component of the fiber laser marking machine is the fiber laser, which uses glass fiber doped with rare earth elements (such as ytterbium) as the gain medium. The laser converts electrical energy into light energy through a pump source (such as a laser diode), exciting rare earth elements in the fiber to produce stimulated radiation. This radiation is reflected and amplified back and forth in an optical resonant cavity, ultimately forming a laser beam with high monochromaticity, high coherence, and high directionality. The laser wavelength output by fiber lasers is usually 1064nm, which has good absorption characteristics for both metallic and non-metallic materials, providing a foundation for subsequent marking.
2、 Process of action: interaction between laser and material
When a high-energy density laser beam is projected onto the surface of a material, the material rapidly absorbs the laser energy, causing a sharp increase in local temperature. This process can cause various physical and chemical changes in the material, including:
Melting: After the material surface absorbs laser energy, the temperature rises above the melting point, forming a molten state.
Vaporization: As the temperature further increases, the surface substances of the material directly transform from liquid to gas, forming steam.
Oxidation: At high temperatures, the surface of a material undergoes a chemical reaction with oxygen in the air, forming an oxide layer.
Chemical changes: Laser energy may also cause molecular structural changes on the surface of materials, leading to color changes or the formation of new compounds.
These changes work together to form clear markings on the surface of the material. For example, when black marking is applied on the surface of stainless steel, the laser will form a micrometer scale oxide layer on the surface. By controlling the thickness of the oxide layer, different grayscale effects can be achieved.
3、 Key components: Laser transmission and focusing system
The fiber laser marking machine transmits the laser beam from the laser to the marking head through an optical fiber. Fiber optics have the characteristics of stable optical path and low energy loss, which can ensure that laser beams maintain high energy density after long-distance transmission. The marking head includes optical components such as lenses, control mirrors, and scanning mirrors, which work together to focus and scan the laser beam.
Lens: Focus the laser beam onto a very small point on the surface of the material, which has a high energy density and can quickly absorb laser energy.
Control mirror and scanning mirror: By controlling the movement of the mirror, the position and shape of the laser point can be controlled. The scanning mirror is responsible for scanning the laser beam along a predetermined path on the surface of the material to complete the marking of complex shapes.
4、 Marking effect: multiple ways to achieve permanent marking
Fiber laser marking machine achieves permanent marking through the following three main effects:
Evaporation effect: The high energy of the laser beam rapidly vaporizes the surface material, exposing deeper layers of material. This effect is applicable to marking scenes that require the removal of surface layers to display underlying information.
Physical change effect: Laser energy causes physical changes on the surface of materials (such as melting, solidification, color changes, etc.), thereby engraving the desired pattern or text. This effect is applicable to the scenario of modifying the surface of materials to achieve labeling.
Ablation effect: The laser beam burns off some material, revealing the desired etched pattern or text. This effect applies to scenarios where material needs to be directly removed to form a mark.